| Include Page | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Expand | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
What is ANSYS?ANSYS is a finite-element analysis package used widely in industry to simulate the response of a physical system to structural loading, and thermal and electromagnetic effects. ANSYS uses the finite-element method to solve the underlying governing equations and the associated problem-specific boundary conditions |
| Table of Contents |
|---|
List of Learning Modules
These learning modules progress from simple to more complex. If you are unfamiliar with ANSYS, please begin with the first module.
Basic Learning Modules:
| |
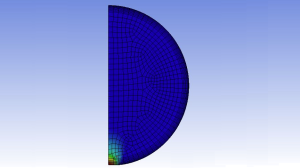
| Plate with a hole |
| |
| Three-dimensional curved beam |
| Vibration analysis of a frame |
|
Intermediate Learning Modules:
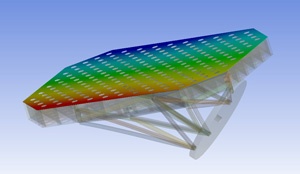
| Semi-monocoque shell |
| Semi-monocoque shell, Part 2: Parametric study |
| Orthotropic plate with a hole |
| Disks in point contact |
...
. About the ANSYS learning modulesThis ANSYS short course consists of a set of learning modules on using ANSYS to solve problems in solid mechanics. The learning modules lead the user through the steps involved in solving a selected set of problems using ANSYS. We not only provide the solution steps but also the rationale behind them. It is worthwhile for the user to understand the underlying concepts as she goes through the learning modules in order to be able to correctly apply ANSYS to other problems. The user would be ill-served by clicking through the learning modules in zombie-mode. Each learning module is followed by problems which are geared towards strengthening and reinforcing the knowledge and understanding gained in the learning modules. Working through the problem sets is an intrinsic part of the learning process and shouldn't be skipped. These learning modules have been developed by |
...
...
in the Sibley School of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering |
...
at Cornell University. The Swanson Engineering Simulation Program has been established with the goal of integrating computer-based simulations into the mechanical engineering curriculum. This program has been endowed by Dr. John Swanson, the founder |
...
of ANSYS Inc. |
...
and an alumnus of the Sibley School. The development of these learning modules is being supported by |
...
...
award from Cornell University. |
What is ANSYS?
ANSYS is a finite-element analysis package used widely in industry to simulate the response of a physical system to structural loading, and thermal and electromagnetic effects. ANSYS uses the finite-element method to solve the underlying governing equations and the associated problem-specific boundary conditions.
How to use these learning modules
These learning modules are designed to be used online and run side-by-side with the ANSYS software. After you launch the learning modules and ANSYS, you will have to drag the browser window to the width of the largest image (about 350 pixels). To make best use of screen real estate, move the windows around and resize them so that you approximate this screen arrangement.
System and software requirements
- System: Any system that can run ANSYS and a web browser.
- Screen: Resolution should be at least 1280 x 1024 pixels for optimal viewing. A 17" monitor or larger is recommended.
- ANSYS version 7.0. These tutorials were created using ANSYS 7.0.
- Web Browser: These tutorials work best in 5.0 or higher versions of Internet Explorer and Netscape because style sheet support is needed. These tutorials can be used with Netscape 4.x but may not render correctly.
Choose a learning module by selecting from the list at the top of this page
Conventions used
Each learning module begins with a problem specification. A solution can be obtained by following these nine steps:
1. Start-up and preliminary set-up
2. Specify element type and constants
3. Specify material properties
4. Specify geometry
5. Mesh geometry
6. Specify boundary conditions
7. Solve!
8. Postprocess the results
9. Validate the results
These steps appear at the top of each page of the learning module with the current step highlighted in red.
ANSYS uses cascading menus which are represented as follows:
Main Menu > Preprocessor > Material Props > Material Models ....
This means that in the Main Menu, click on Preprocessor. Then, in the Preprocessor menu that comes up, click on Material Props and so on.
Names of windows are in italics.
Items and options appearing within menus and dialog boxes are purple, italic, and bold.
Text and numbers that need to be entered are indicated in Courier font.
List of Learning ModulesEach learning module below contains a step-by-step tutorial that shows details of how to solve a selected problem using ANSYS, a popular tool for finite-element analysis (FEA). The tutorial topics are drawn from Cornell University courses, the Prantil et al textbook, student/research projects etc. If a tutorial is from a course, the relevant course number is indicated below. All tutorials have a common structure and use the same high-level steps starting with Pre-Analysis and ending with Verification and Validation . Pre-Analysis includes hand calculations to predict expected results while Verification and Validation can be thought of as a formal process for checking computer results. Both these steps are extremely important in practice though often overlooked. The pedagogical philosophy behind these modules is discussed in this article from the ANSYS Advantage magazine. |
Finite Element Analysis Using ANSYS Mechanical
The following ANSYS tutorials show you how to obtain an FEA solution from scratch using ANSYS Mechanical.
Introductory Tutorials
Static Structural | |||
Static Structural | |||
Static Structural | |||
Static Structural | |||
Static Structural | |||
Prantil et al textbook | Static Structural | ||
Prantil et al textbook | Static Structural | ||
Prantil et al textbook | Static Structural | ||
Prantil et al textbook | Static Structural | ||
Prantil et al textbook | Static Structural | ||
Three-dimensional analysis of | Prantil et al textbook | Static Structural | |
Optimization | |||
Heat Transfer | |||
Heat Transfer | |||
Dynamics | |||
| Dynamics |
Finite Element Analysis Using ANSYS Mechanical: Results-Interpretation
The following ANSYS tutorials focus on the interpretation and verification of FEA results (rather than on obtaining an FEA solution from scratch). The ANSYS solution files are provided as a download. We read the solution into ANSYS Mechanical and then move directly to reviewing the results critically. We are particularly interested in the comparison of FEA results with hand calculations.
Static Structural | |||
Static Structural | |||
Static Structural |
Advanced Tutorials
Static Structural | |||
Static Structural | |||
Under Construction |
| Static Structural | |
Static Structural
| |||
Static Structural | |||
Undergrad Project | Static Structural | ||
| Static Structural | ||
CCAT Telescope | Static Structural | ||
Static Structural | |||
| MAE 4020-5020 | Static Structural, FSI | ||
| Structural | ||
| Coupled Static | ||
| Heat Transfer | ||
| Heat Transfer | ||
| Heat Transfer | ||
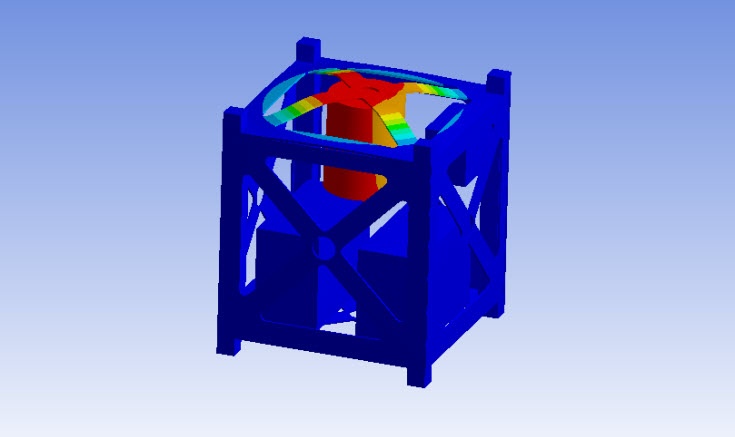
Cornell CubeSat Team | Dynamics | ||
Cornell Formula |
|
Tips and tricks
Finite Element Analysis Using ANSYS APDL (These tutorials are no longer being updated)
ANSYS 11.0 12.0 APDL | Basic | ||
ANSYS 11.0 12.0 APDL | Basic | ||
ANSYS 12.0 APDL | Intermediate | ||
ANSYS 11.0 APDL | Intermediate | ||
ANSYS 7.0 | Intermediate | ||
ANSYS 10.0 APDL | Intermediate | ||
ANSYS 10.0 APDL | Intermediate | ||
ANSYS 11.0 12.0 APDL | Intermediate | ||
ANSYS 7.1 Classic | Intermediate |
 Sign-up for free online course on ANSYS simulations!
Sign-up for free online course on ANSYS simulations!