Author: Rajesh Bhaskaran, Cornell University
Laminar Pipe Flow
Created using ANSYS 16.2
Learning Goals
In this module, you'll learn to:
- Develop the numerical solution to a laminar pipe flow problem in ANSYS Fluent
- Verify the numerical results from ANSYS Fluent
- Connect the ANSYS steps to concepts covered in the Computational Fluid Dynamics section
Problem Specification
This module is drawn from MAE 4230/5230 Intermediate Fluid Dynamics at Cornell University.
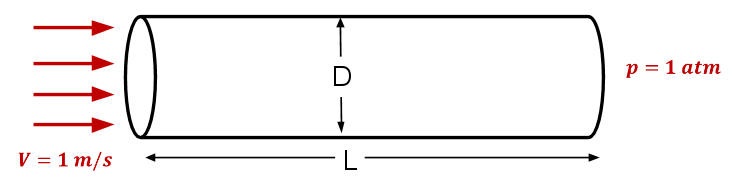
Consider fluid flowing through a circular pipe of constant radius as illustrated below. The figure is not to scale. The pipe diameter D = 0.2 m and length L = 3 m Consider the inlet velocity to be constant over the cross-section and equal to 1 m/s. The pressure at the pipe outlet is 1 atm. Take density ρ = 1 kg/ m 3 and coefficient of viscosity µ = 2 x 10 -3 kg/(m*s). These parameters have been chosen to get a desired Reynolds number of 100 and don't correspond to any real fluid.
We'll solve this problem numerically using ANSYS Fluent. We'll look at the following results:
Velocity vectors
Velocity magnitude contours
Pressure contours
Velocity profile at the outlet
We'll verify the results by following a systematic process which includes comparing the results with the analytical solution in the full-developed region.
 Sign-up for free online course on ANSYS simulations!
Sign-up for free online course on ANSYS simulations!