Step 2: Geometry
Care to skip the geometry and meshing processes? README
If you would prefer to skip the geometry and mesh processes, then you can download the files here. Download the "zip" file, then "unzip" the file. Then, extract the "pipe_laminar" folder and the "pipe_laminar.wbpj" file to the desktop. Lastly, double click the "pipe_laminar.wbpj" file (located on the desktop) to launch ANSYS Workbench with the desired geometry and mesh files. Then, click here to skip ahead to Step 4 of the tutorial.
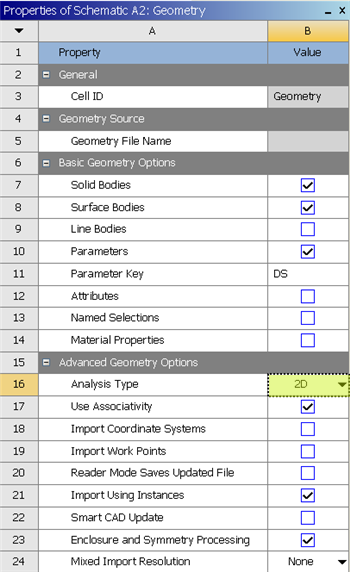
In the Project Schematic of the Workbench window, right click on Geometry and select Properties, as shown below.
The properties menu will then appear to the right of the Workbench window. Under Advance Geometry Options, change the Analysis Type to 2D as shown in the image below.
In the Project Schematic, double click on Geometry to start preparing the geometry. This tutorial is specially configured, so the user can have both the tutorial and ANSYS open at the same time as shown below. It will be beneficial to have both ANSYS and your internet browser displayed on your monitor. Your internet browser should consume approximately one third of the screen width while ANSYS should take the other two thirds.
At this point, a new window, ANSYS Design Modeler will be opened. You will be asked to select desired length unit. Use the default meter unit and click OK.
Creating a Sketch
Start by creating a sketch on the XYPlane. Under Tree Outline, select XYPlane, then click on Sketching right before Details View. This will bring up the Sketching Toolboxes.
Click on the +Z axis on the bottom right corner of the Graphics window to have a normal look of the XY Plane.
In the Sketching toolboxes, select Rectangle. In the Graphics window, create a rough Rectangle from starting from the origin in the positive XY direction (Make sure that you see a letter P at the origin before you start dragging the rectangle. The letter P at the origin means the geometry is constrained at the origin.)
You should have something like this:
Note: You do not have to worry about geometry for now, we can dimension them properly in the later step.
Dimensions and Constraints
Now we will specify the appropriate dimensions and constraints.
Under Sketching Toolboxes, select Dimensions tab, use the default dimensioning tools. Dimension the geometry as shown:
insert geometry dimension
Under Details View on the lower left corner, input the value for dimension appropriately.
V1: 0.1 m
H2: 8 m
Now that we have the sketch done, we can create a surface for this sketch.
Concept>Surfaces From Sketches
This will create a new surface SurfaceSK1. Under Details View, select Sketch1 as Base Objects and then under Surface body select the thickness to 0.1m and click Apply. Finally click Generate to generate the surface.
You can close the Design Modeler and go back to Workbench (Don't worry, it will auto save).
Go to Step 3: Mesh
 Sign-up for free online course on ANSYS simulations!
Sign-up for free online course on ANSYS simulations!