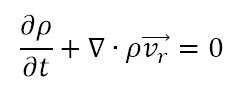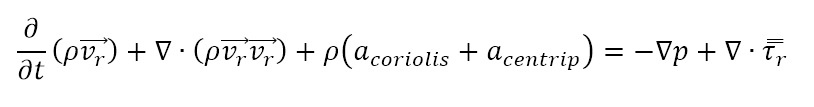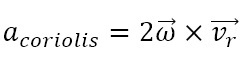...
- Conservation of Mass:
- Navier-Stokes equations, simplified for constant angular velocity
where:
and
FLUENT will solve this in a moving frame of reference. This is a good simplification, because with it we don't have to deal with moving mesh. (yet! Keep checking for future tutorials on that!)
Note that we're solving a turbulent problem, and we will assume k-epsilon model with default FLUENT values
Boundary Conditions
The boundary conditions are:
- Inlet (far-field): constant velocity in the x-direction of 10m/s, with turbulent intensity of 5% and turbulent viscosity ratio of 1.
- Outlet (far-field): absolute pressure of 101325 Pa, or 1 atm, with same turbulent parameters as above.
- Blades: wall, so no velocity. (No-slip condition).
...
Numerical Solution Procedure in ANSYS
...
 Sign-up for free online course on ANSYS simulations!
Sign-up for free online course on ANSYS simulations!