...
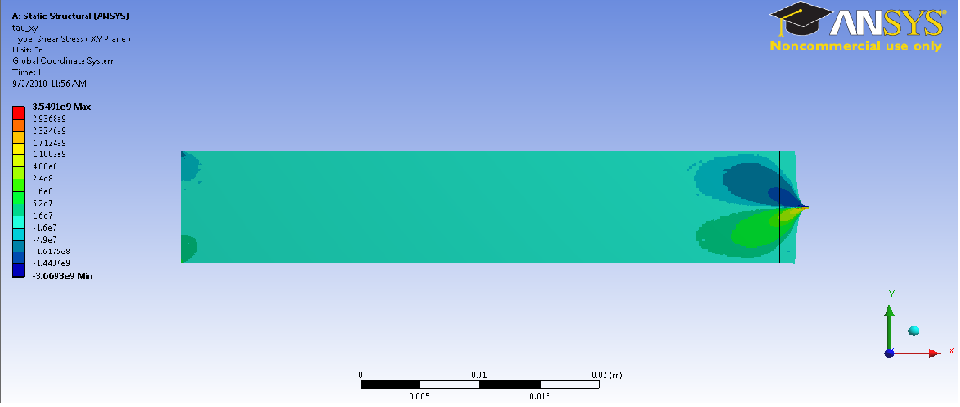
Note here that the stress in x direction is not constant as assumed in the analytical method. The point load at the end of the bar means the stress will be greater If we were to pick a section near the middle of the bar, our analytical result would be nearly accurate. The solution, however, no longer applies when considering the stresses at the wall on the top and bottom of the bar. There are also higher stresses in the area close to the wall, and the stresses near the point load. Obviously, the stresses in the x-direction maximizes at the point load.
Sigma_y:
The analytical method assumed a long bar, therefore by definition, the stresses in the y direction are assumed to be zero. From the simulation, it is clear to see this is obviously not the caseSince this bar does have width, the stresses in the y direction are symmetrical about the middle axis.
Tau_xy:
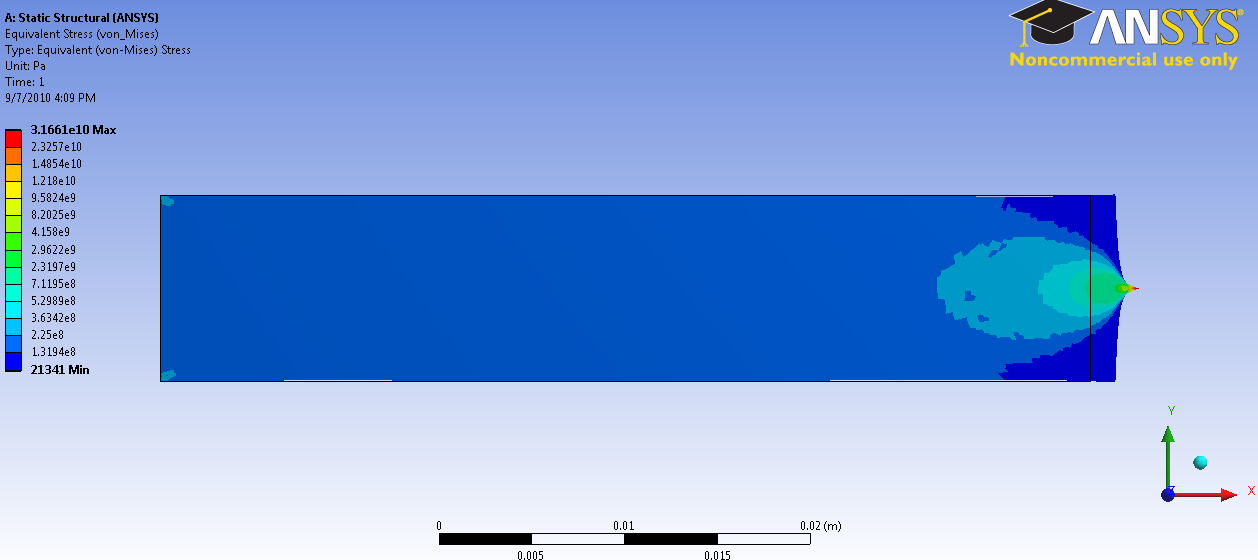
Von Mises:
Von Mises stress is used to predict yielding of the material. We can consider the maximum and minimum von mises stress as the critical design points. For example, in this case, we would want to reinforce the point where the load is applied to prevent reaching the tensile limit load of the material.
...
 Sign-up for free online course on ANSYS simulations!
Sign-up for free online course on ANSYS simulations!