...
| Note |
|---|
In ANSYS version 14.5 and later, only one half of the pipe cross-section is displayed after using the mirroring option. You can work around this by applying the mirroring condition in the "Default transform" setting and not in the "View" Tab. To do this select "Default Transform" in the left-hand menu, uncheck "Instancing Info from Domain", check "Apply Reflection" and select to mirror about the ZX Plane. |
...
The Nusselt number is a non-dimensional parameter that provides a measure of the convection heat transfer at a surface. It is the ratio of convection to pure conduction heat transfer. We will now derive the Nusselt number as a function of the given parameters and temperature.
The convection heat transfer at the pipe wall is:
We can rearrange terms to find an expression for h, the convection coefficient:
Substitute the convection coefficient expression into the Nusselt Number expression:
where
h is the convection coefficient.
k is the thermal conductivity.
L is the length scale. Similar to the Reynold's Number, the length scale is the diameter of the pipe for an internal pipe flow.
q''_w is the heat flux at the heated surface, 37.5 W/m^2.
Tw is the pipe wall temperature at a given location along the pipe.
Tm is the mean temperature in the pipe at the location where Tw is defined.
Wall Temperature
To find the temperature at the wall, click on insert >> location >> point, and name it Tw exit. In the Details of Tw exit window, set Method to XYZ and enter (8.64, 0.06, 0) in Point.Click Apply to create a point at the upper right corner of the pipe.
Click on Expression right below and right click in the window to create a new expression named Tw. Under Details of Tw panel, enter probe maxVal(Temperature)@Tw exit in the Definition tab.
Tw now gives the temperature at the location (8.64, 0.06, 0), which is on the exit pipe wall.
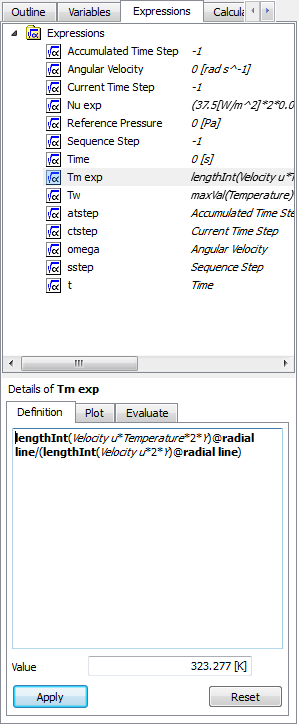
Mixed Mean Temperature
To find the mean temperature at a given location in the pipe, click on insert >> location >> line, and name it exit. In the Details of exit window, set Method to Two Points and enter (8.64, 0, 0) for Point 1 and (8.64, 0.06, 0) for Point 2. Click Apply to create a line at the exit of the pipe. The mean temperature is the area weighted average temperature and we can use integral to find the appropriate mean Temperature:
...
This expression will now give the mean temperature at the location in which we called "exit". Recall the pipe radius r is defined in the Y direction in FLUENT. Hence we will use Y to define the radial position in the pipe, as shown in the expression above.
Nusselt Number
We are now ready to find the Nusselt Number. Create another expression and name it Nu exitexp. Under the Definition tab, enter the Nusselt Number expression shown in the equation above. The units are entered in square brackets, this is done to ensure the expression for the Nusselt Number is dimensionless.
| Note |
|---|
You may get a slightly higher or lower value for the Nusselt Number here. |
We would like to compare the Nusselt Number along the heated section of the pipe. We can generate the Nusselt Number at a different location by simply changing the x-coordinate of exit and Tw exit, which we defined earlier. Once the new coordinates defined in exit and Tw exit are updated, the associated expression Tw, Tm, and Nu exit will exp will be updated automatically.
...
Go to all FLUENT Learning Modules
 Sign-up for free online course on ANSYS simulations!
Sign-up for free online course on ANSYS simulations!