...
In the window that comes up, enter the location of the folder you just created as your Working Directory by browsing to it. All files generated during the ANSYS run will be stored in this directory.
Specify crank as your Job Name. The job name is the prefix used for all files generated during the ANSYS session. For example, when you perform a save operation in ANSYS, it'll store your work in a file called crank.db in your working directory.
For this tutorial, we'll use the default values for the other fields. Click Run. This brings up the ANSYS interface. To make best use of screen real estate, move the windows around and resize them so that you approximate this screen arrangement. This way you can read instructions in the browser window and implement them in ANSYS. Note that this tutorial has been formatted to fit in a skinny browser window. If your monitor screen is small, you can use Alt+Tab keys to conveniently switch between the ANSYS and browser windows (this trick works in Microsoft Windows).
...
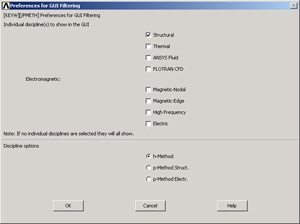
In the Preferences for GUI Filtering dialog box, click on the box next to Structural so that a tick mark appears in the box. Click OK.
Recall that this is an optional step that customizes the graphical user interface so that only menu options valid for structural problems are made available during the ANSYS session.
...
 Sign-up for free online course on ANSYS simulations!
Sign-up for free online course on ANSYS simulations!