Connect to the Server
- Run the following command, where -L mean to forward server's port to local. Because Kubernetes exposes port 6445, we would like to forward it to localhost:6443. The username should just be your Cornell NetID (it's easier to memorize). An admin account holder should be able to create the linux account for you.
ssh -i -L 6445:localhost:6443 username@ssh.diaper-project.com
- You should see a pop-up looks like this, which means that you have already connected to the server.
Connect to Kubernetes
- We first need to install Kubernetes on our local machine. To install using Docker (you might want to use Docker to build images), check out Install and turn on Kubernetes.
- There are various UI explorers for Kubernetes, one of my favorites is called k9s. To install, check out Install (k9scli.io).
- Add the server cluster credentials in the Kubernetes config file. The configuration is as follows:
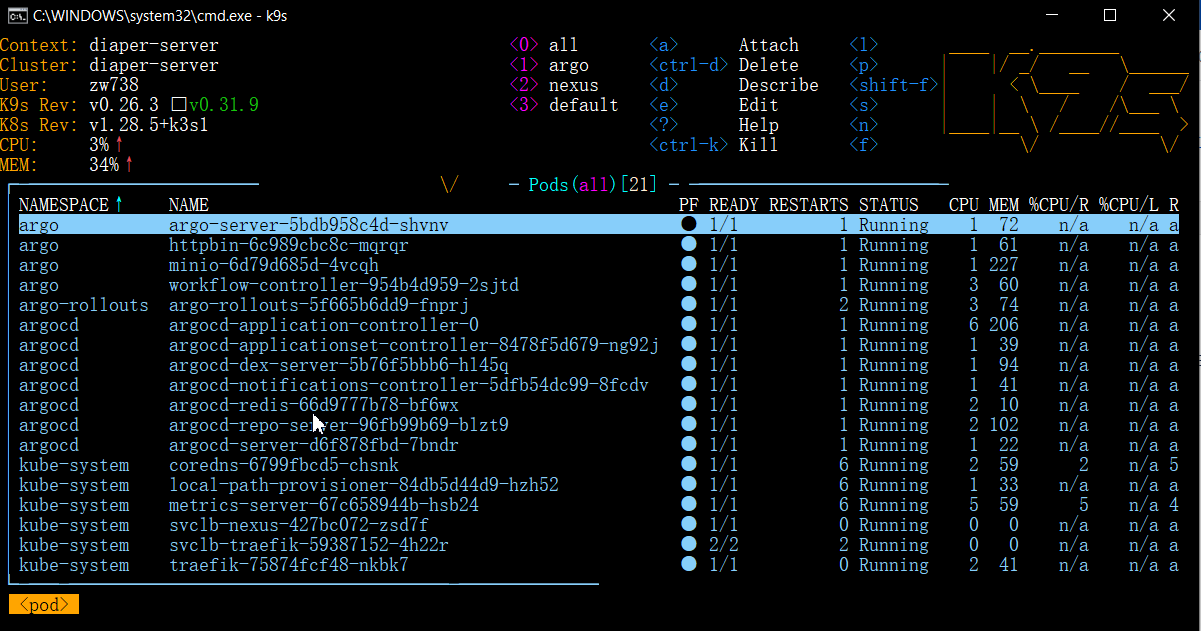
- After adding the configs, you should be able to connect to the Kubernetes cluster using k9s. If your k9s is under one of the environments $PATH, you can simply run: k9s on any command line interface. It looks like the following:
If you don't see all pods running, it is probably because you're viewing a specific namespace. You can simply press '0' to view pods in all namespaces.
- To navigate between Services, Deployments, or Pods, you can type
:services or :deployments or :pods
- To port-forward a pod, type shift+F. To view the log, type l. To kill a pod, type ctrl+k.... You can always view these commands by typing ?(question mark).
More k9s Tutorial: derailed/k9s: 🐶 Kubernetes CLI To Manage Your Clusters In Style! (github.com)