|
Problem Specification. |
Launch FLUENT
Start > Programs > Fluent Inc > FLUENT 6.3.26
Select 2ddp from the list of options and click Run.
Import File
Main Menu > File > Read > Case...
Navigate to your working directory and select the cylinder.msh file. Click OK.
Analyze Grid
Grid > Info > Size
Check how many cells and nodes the mesh has.
Display > Grid
Display the grid information.
Define Properties
Define > Models > Solver...
Under the Solver box, select Pressure Based.
Click OK.
Define > Models > Viscous
Select Laminar under Model
Click OK.
Define > Models > Energy
Do not select Energy Equation.
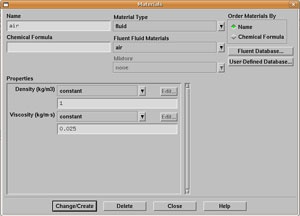
Define > Materials
Make sure air is selected under Fluent Fluid Materials. Set Density to constant and equal to 1 kg/m 3 and Viscosity to 0.025 kg/m-s. We choose these numbers so that Re = 40.

Click Change/Create.
Define > Operating Conditions
We'll work in terms of gauge pressures in this example. So set Operating Pressure to the ambient value of 101,325 Pa.
Click OK.
Define > Boundary Conditions
Set inlet, click Set... and set the Velocity Magnitude to 1 m/s. Click OK.
Set outlet, click Set... and set the Gauge Pressure at this boundary to 0. Click OK.
Go to Step 5: Solve.
See and rate the complete learning module.
Go to all FLUENT Learning Modules