...
| Panel |
|---|
Author: John Singleton and Rajesh Bhaskaran, Cornell University Problem Specification |
...
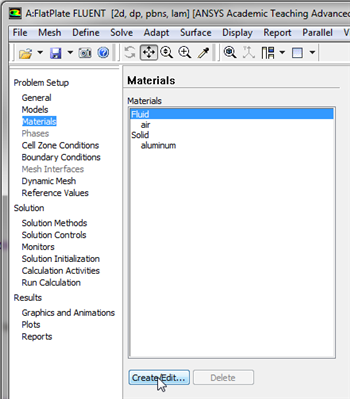
Now, the properties of the fluid that is being modeled will be specified. The properties of the fluid were specified in the Problem Specification section. In order to create a new fluid (Click) Materials > Fluid > Create/Edit... as shown in the image below.
| newwindow | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
https://confluence.cornell.edu/download/attachments/118771050/CreateFluid_Full.png |
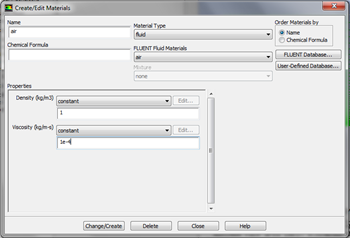
In the Create/Edit Materials menu set the Density to 1kg/m^3 (constant) and set the Viscosity to 1e-4 kg/(ms) (constant) as shown in the image below.
| newwindow | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
https://confluence.cornell.edu/download/attachments/118771050/Mat1_Full.png |
Click Change/Create. Close the window.
...
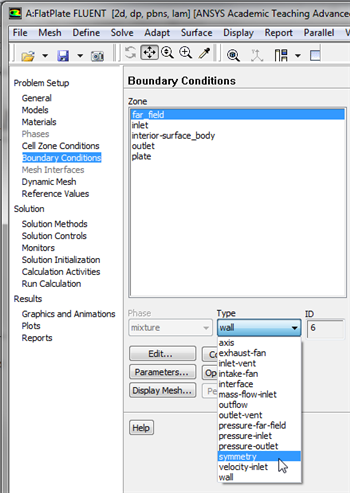
For the far_field, set the Boundary Condition Type to symmetry, as shown below.
| newwindow | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
https://confluence.cornell.edu/download/attachments/118771050/symmbc_Full.png |
In the first dialog box click yes and in the second dialog box leave the name as is and click OK. The symmetry boundary conditions sets the velocities normal to the boundary equal to zero.
At this point save your work in the FLUENT Window by clicking the save button, .
Go to Step 5: Solution
See and rate the complete Learning Module
Go to all FLUENT Learning Modules
 Sign-up for free online course on ANSYS simulations!
Sign-up for free online course on ANSYS simulations!