...
In the above example, there are three functions: the main function is called newsstats. Within this function, there are two subfunctions; one called "mean" and the other, "median". The subfunction is defined the exact same way as the main function; but the difference is that the subfunction is available to functions in this M-file only - you cannot call your subfunctions in the command window. In the above example, the main function calls both of the subfunctions, making the code much shorter and simpler. For longer, more complex code, this can save you a lot of debugging time by breaking down your code into smaller pieces.
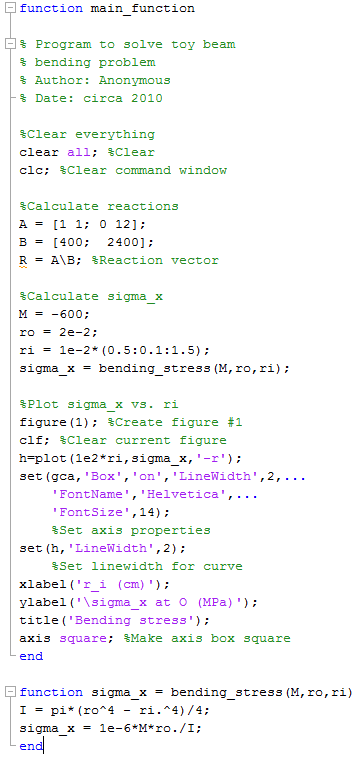
Open up beam5.m. We will use the subfunction concept to incorporate the main program (beam5.m) and the function bending_stress into one M-file. We are going to designate beam5.m as a function. So at the top of the code, include the following code:
...
Click save as - and name the file "main_function" - the same as the function's name. Now, open up bending_stress.m and copy the entire code. Paste it below the main function. Close both functions with an "end" What you have now should look like this:
Now, run main_function in the command window. The result should be the same plot you saw when you ran beam3.m and beam5.m.
That brings us to the end of this tour. Before we part, let's remind ourselves of some important programming guidelines that we have followed in this tour:
...
 Sign-up for free online course on ANSYS simulations!
Sign-up for free online course on ANSYS simulations!