| Wiki Markup |
|---|
{panel}
|
| Panel |
We will patch the upper region downstream of the flow to create asymmetry so that we can obtain stable oscillation of vortex shedding faster.
To do this, we will create a register to patch the Y velocity in downstream of cylinder.
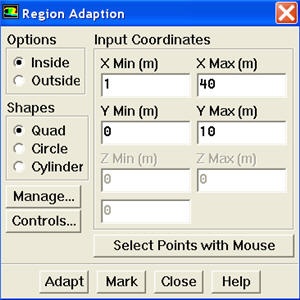
Main Menu > Adapt > Region...
Enter 1 and 40 for X Min and X Max. Enter 0 and 10 for Y Min and Y Max. Click Mark. FLUENT will print the following message in the console window:
5416 cells marked for refinement, 0 cells marked for coarsening
Close the Region Adaption panel.
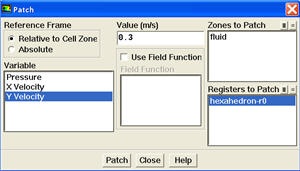
We will now patch Y velocity in the registered region.
Main Menu > Solve > Initializate > Patch...
| newwindow | ||
|---|---|---|
| Higher Resolution Image | Higher Resolution Image | Author: Rajesh Bhaskaran & Yong Sheng Khoo, CornellUniversity Problem Specification |
Step 5: Solve!
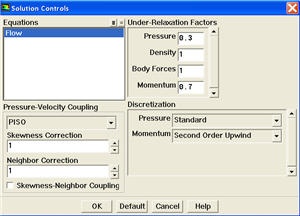
Set Solution Controls
Main Menu > Solve > Controls > Solution...
Select PISO from the Pressure-Velocity Coupling drop-down list.
...
PISO allows the use of higher time step size without affecting the stability of the solution. Hence it is recommended pressure-velocity coupling for solving transient applications.
Uncheck Skewnes-Neighbor Coupling.
Select Second Order Upwind from the Momentum drop-down list in the Discretization group box. Click OK to close the Solution Controls panel.
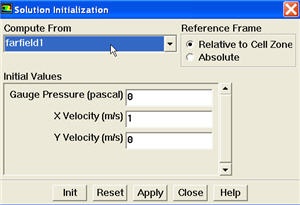
Set Initial Guess
Initialize the flow field to the values at the inlet:
Main Menu > Solve > Initialize > Initialize...
In the Solution Initialization menu that comes up, choose inlet under Compute From. The X Velocity for all cells will be set to 1 m/s, the Y Velocity to 0 m/s and the Gauge Pressure to 0 Pa. These values have been taken from the inlet boundary condition.
Click Init. This completes the initialization. Close the window.
Patch Region
University
[Problem Specification|FLUENT - Unsteady Flow Past a Cylinder - Problem Specification]\\ [1. Create Geometry in GAMBIT|Fluent - Unsteady Flow Past a Cylinder - Step 1]\\
[2. Mesh Geometry in GAMBIT|FLUENT - Unsteady Flow Past a Cylinder - Step 2]\\
[3. Specify Boundary Types in GAMBIT|FLUENT - Unsteady Flow Past a Cylinder - Step 3]\\
[4. Set Up Problem in FLUENT|FLUENT - Unsteady Flow Past a Cylinder - Step 4]\\ {color:#ff0000}{*}5. Solve\!*{color}
[6. Analyze Results|FLUENT - Unsteady Flow Past a Cylinder - Step 6]\\
[7. Refine Mesh|FLUENT - Unsteady Flow Past a Cylinder - Step 7]\\
{panel}
{dynamictable:UniqueName\|title=Table Title} \|\|header1\|\|header2\|\|header3\|\| {dynamictable}
h2. Step 5: Solve\!
h4. Set Solution Controls
*Main Menu > Solve > Controls > Solution...*
!solution control.jpg!
Select {color:#660099}{*}{_}PISO{_}{*}{color} from the {color:#660099}{*}{_}Pressure-Velocity Coupling{_}{*}{color} drop-down list.
{info:title= }PISO allows the use of higher time step size without affecting the stability of the solution. Hence it is recommended pressure-velocity coupling for solving transient applications.
{info}
Uncheck {color:#660099}{*}{_}Skewnes-Neighbor Coupling{_}{*}{color}.
Select {color:#660099}{*}{_}Second Order Upwind{_}{*}{color} from the Momentum drop-down list in the {color:#660099}{*}{_}Discretization{_}{*}{color} group box. Click {color:#660099}{*}{_}OK{_}{*}{color} to close the {color:#660099}{*}{_}Solution Controls{_}{*}{color} panel.
\\
h4. Set Initial Guess
Initialize the flow field to the values at the inlet:
*Main Menu > Solve > Initialize > Initialize...*
In the _Solution Initialization_ menu that comes up, choose {color:#660099}{*}{_}inlet{_}{*}{color} under {color:#660099}{*}{_}Compute From{_}{*}{color}. The {color:#660099}{*}{_}X Velocity{_}{*}{color} for _all_ cells will be set to 1 m/s, the {color:#660099}{*}{_}Y{_}{*}{color} {color:#660099}{*}{_}Velocity{_}{*}{color} to 0 m/s and the {color:#660099}{*}{_}Gauge Pressure{_}{*}{color} to 0 Pa. These values have been taken from the inlet boundary condition.
!Initialize.jpg!
Click {color:#660099}{*}{_}Init{_}{*}{color}. This completes the initialization. {color:#660099}{*}{_}Close{_}{*}{color} the window.
\\
h4. Patch Region
We will patch the upper region downstream of the flow to create asymmetry so that we can obtain stable oscillation of vortex shedding faster.
To do this, we will create a register to patch the Y velocity in downstream of cylinder.
*Main Menu > Adapt > Region...*
\\ !Region Adaption.jpg!
Enter {{1}} and {{40}} for {color:#660099}{*}{_}X Min{_}{*}{color} and {color:#660099}{*}{_}X Max{_}{*}{color}. Enter {{0}} and {{10}} for {color:#660099}{*}{_}Y Min{_}{*}{color} and {color:#660099}{*}{_}Y Max{_}{*}{color}. Click {color:#660099}{*}{_}Mark{_}{*}{color}. FLUENT will print the following message in the console window:
{{{_}5416 cells marked for refinement, 0 cells marked for coarsening{_}}}
{color:#660099}{*}{_}Close{_}{*}{color} the _Region Adaption_ panel.
We will now patch Y velocity in the registered region.
*Main Menu > Solve > Initializate > Patch...*
\\ !patch_sm.jpg!
{newwindow:Higher Resolution Image}https://confluence.cornell.edu/download/attachments/107011456/patch.jpg |
...
{newwindow} Select {color:#660099}{*}{_}hexahedron-r0{_}{*}{color} from the {color:#660099}{*}{_}Registers to Patch{_}{*}{color}. Select {color:#660099}{*}{_}Y Velocity{_}{*}{color} from the {color:#660099}{*}{_}Variable{_}{*}{color} selection list. Enter {{0.3}} for {color:#660099}{*}{_}Value{_}{*}{color}. Click {color:#660099}{*}{_}Patch |
...
See and rate the complete Learning Module
...
{_}{*}{color}.
\\
*[*Go to Step 6: Analyze Results*|FLUENT - Unsteady Flow Past a Cylinder - Step 6]*
[See and rate the complete Learning Module|FLUENT - Unsteady Flow Past a Cylinder]
Go to [all FLUENT Learning Modules|FLUENT Learning Modules] |
 Sign-up for free online course on ANSYS simulations!
Sign-up for free online course on ANSYS simulations!