| Include Page | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Include Page | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Info |
|---|
This module is from our free online simulations course at edX.org (sign up here). The edX interface provides a better user experience, so we have moved the module there. |
Laminar Pipe Flow
Created using ANSYS 13.0. Tutorial instructions work with ANSYS 14.0 and 15.0. There are minor layout changes in ANSYS 15.0.
Problem Specification
...
16.2
Learning Goals
In this module, you'll learn to:
- Develop the numerical solution to a laminar pipe flow problem in ANSYS Fluent
- Verify the numerical results from ANSYS Fluent
- Connect the ANSYS steps to concepts covered in the Computational Fluid Dynamics section
Problem Specification
This module is drawn from MAE 4230/5230 Intermediate Fluid Dynamics at Cornell University.
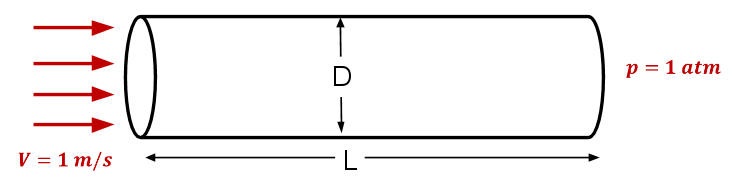
Consider fluid flowing through a circular pipe of constant radius as illustrated
...
below.
...
The figure is not to scale. The pipe
...
diameter D = 0.2 m and
...
length L =
...
3 m Consider the inlet velocity to be constant over the cross-section and equal to 1 m/s. The pressure at the pipe outlet is 1 atm. Take
...
density ρ = 1 kg/ m
...
3 and coefficient of
...
viscosity µ = 2 x 10 -
...
3 kg/(m*s). These parameters have been chosen to get a desired Reynolds number of 100 and don't correspond to any real fluid.
...
We'll solve this problem numerically using ANSYS
...
Fluent. We'll look at the following results:
Velocity
vectorsvectors
Velocity magnitude contours
Pressure contours
Velocity profile at the outlet
- Skin friction coefficient along the wall
...
We'll verify the results by following a systematic process which includes comparing the results with the analytical solution in the full-developed
...
region.
Go to Step 1: Pre-Analysis & Start-Upto the EdX course
 Sign-up for free online course on ANSYS simulations!
Sign-up for free online course on ANSYS simulations!