Step 8: Postprocess the Results
Enter the postprocessing module to analyze the solution.
Main Menu > General Postproc
Plot Nodal Solution of Von Mises Stress
Main Menu > General Postproc > Plot results > Contour Plot > Nodal Solu
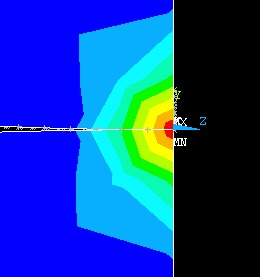
This brings up the Contour Nodal Solution Data menu. Select Stress from the left list, von Mises SEQV from the right list and click OK. Zoom in at the point of contact.
The contour plot also shows the locations of the maximum and minimum values with the labels MX and MN, respectively. As you can see, the upper and lower disks have deformed and come into contact.
List Maximum Compressive Stress
To determine the max principal stress we'll list the principal stresses.
Main Menu > General Postproc > List Results > Nodal Solution
This brings up the List Nodal Solution menu. Select Stress from the left list, Principals SPRIN from the right and click OK.
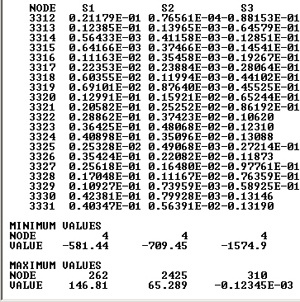
The first three columns list the first, second and third principal stresses at each node. Scroll all the way down in this window.
As you can see, the maximum principal stress is -1574.9. Recall that the the applied force was specified in Newtons (p=4500N) and the geometry in mm. As a result, the max principal stress has units of N/mm2. Also note that the value is negative, which tells us that the max stress is a compressive stress. This is what one would expect based on the loading conditions.
In addition, the max compressive stress is located at node 4 (Third principal stress S3) which belongs to the lower disk and is the node initially in contact with the upper disk. This is also consistent with what one would expect based on the geometry and loading conditions.
List Maximum Displacements
To determine the approach (i.e. total distance through which the two bodies move towards each other as a result of load P) we'll list the displacements of all nodes in the y direction.
Main Menu > General Postproc > List Results > Nodal Solution
This brings up the List Nodal Solution menu. Select DOF solution from the left list, Translation UY from the right and click OK.
The approach can be determined by finding the total displacement of a node attached to the upper surface of the upper disk. Since all the nodes attached to the upper area will be equally displaced as a result of the coupled boundary condition, we can look at the displacement of any node attached to the upper surface.
Nodes 7 and 10 are attached to the upper area of the upper disk. From the list above we can see that the displacement of these nodes is the same and has a value of -0.2525e-01. Recall that the geometry was specified in mm. As a result, the displacement has units of mm. Therefore, the approach or total distance through which the two bodies move towards each other is 0.0252 mm.
 Sign-up for free online course on ANSYS simulations!
Sign-up for free online course on ANSYS simulations!